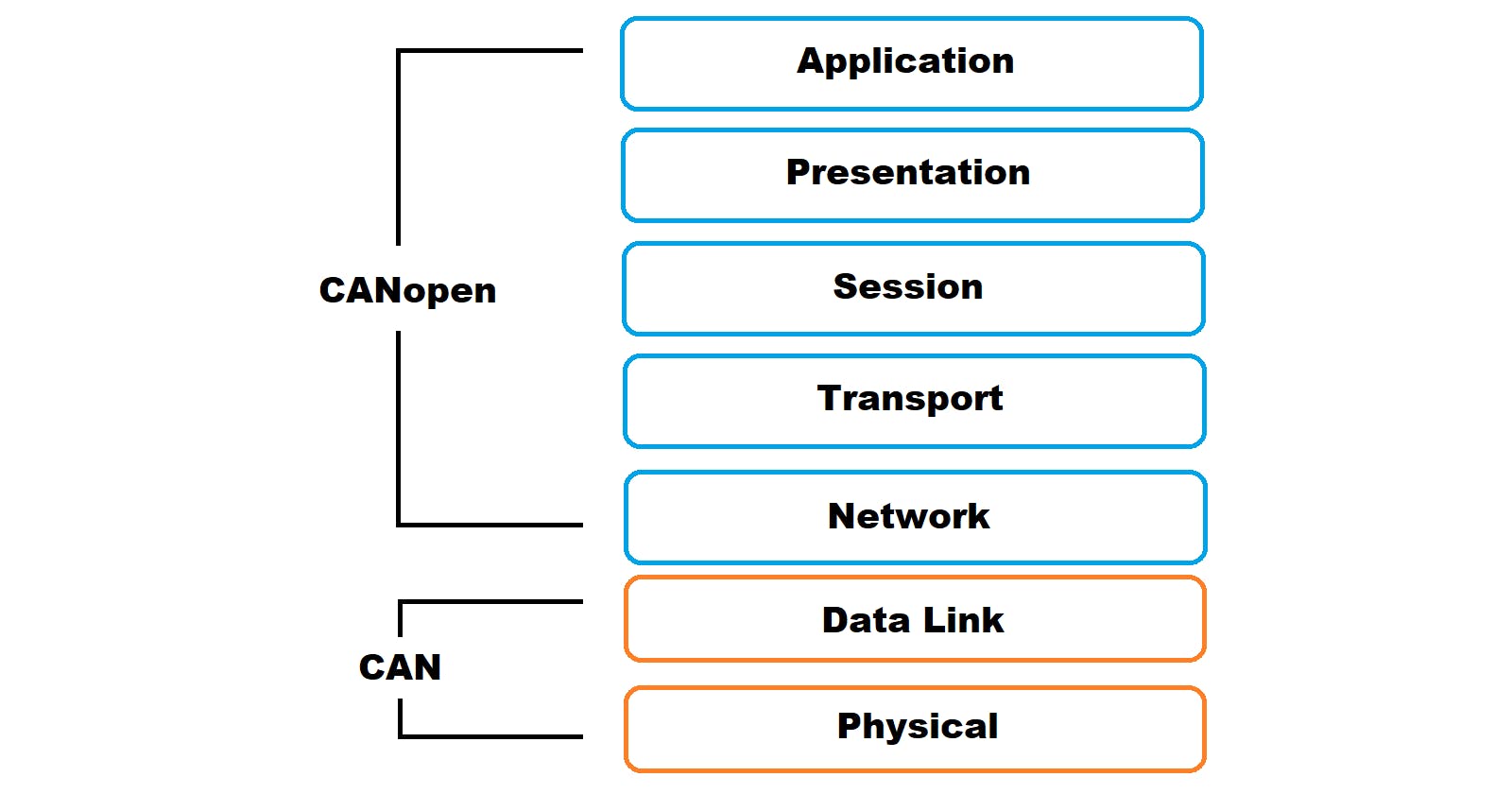
Many CAN protocols are built on top of The CAN(Controller Area Network) bus. CANopen, J1939, UDS are examples of CAN protocols. What is the protocol? From the dictionary, "the official procedure or system of rules governing affairs of state or diplomatic occasions." Then what is the protocol in computing? "a protocol is a set of rules and conventions that define how data is transmitted and received over a network."
CANopen protocol example
The maximum number of nodes that can be supported on CANopen network is 127 nodes.
CANopen supports standard CAN bit rates of 125 kbit/s, 250 kbit/s, and 500 kbit/s, as well as high-speed CAN bit rates of 800 kbit/s, 1 Mbit/s, and 2 Mbit/s.
The node state is defined in NMT(Network Management) as initialization, pre-operational, operational and stopped.
Special function protocols are synchronisation, emergency and time-stamp.
Error control protocols are heartbeat and boot up.
Object dictionary is a standard data structure in CANopen. There are device control objects, communication objects, application objects and manufacturer-specific objects. Commonly, it contains a unique index and sub-index to distinguish each other. Data size and data type and access type are also part of the object dictionary.
Object dictionary entry can be accessed via SDO(Service Data Object) or PDO(Process Data Object). SDO carries a single object dictionary entry and the payload is 4 bytes. PDO can carry multiple object dictionary entries or a single up to 8 bytes of the payload.
SDO requests can be handled when the node state is either pre-operational or operational.
PDO requests can be handled when the node state is operational.