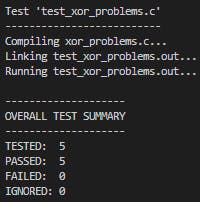
XOR problems
- XOR
Many popular bit manipulation problems require to use XOR in code. In this article, I will introduce couple XOR problems and solution. XOR is represented by ^ in C language. XOR truth table is shown below.
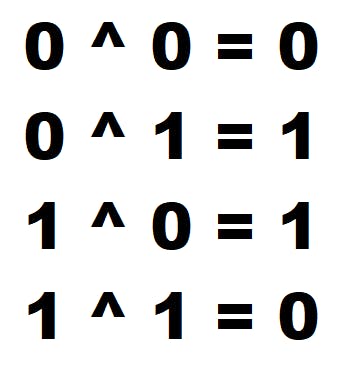 When two bits are the same, result is 0. When two bits are different, result is 1.
When two bits are the same, result is 0. When two bits are different, result is 1.
- Problem1: What is the minimum bit flip to become A from B. A and B are the input of this function. Output is the minimum number of bit flip. Assume A and B are 32-bit integer. Reference: leetcode.com/problems/minimum-bit-flips-to-..
uint32_t problem1(uint32_t A, uint32_t B)
{
uint32_t count = 0;
//Implement logic
return count;
}
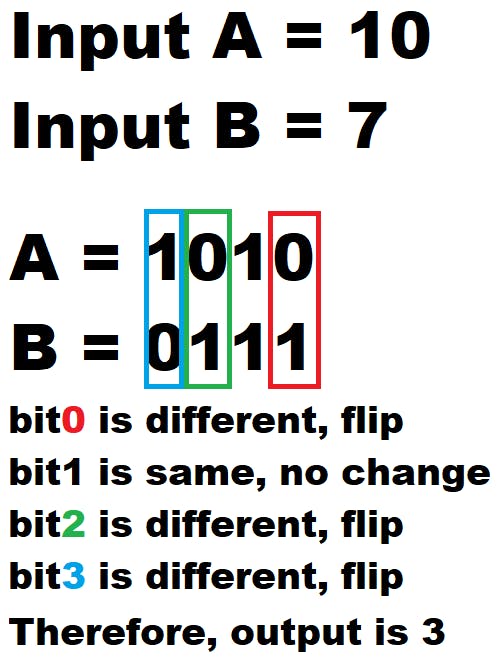
Based on the example above, iterate each bit position XOR result to increase the counter if XOR result is the 1. Another way is finding out number of 1s in A ^ B.
- Implementation and test
Create xor_problems ceedling project
ceedling module:create[xor_problems]xor_problems.h
#ifndef XOR_PROBLEMS_H #define XOR_PROBLEMS_H #include <stdint.h> uint32_t problem1_1(uint32_t A, uint32_t B); uint32_t problem1_2(uint32_t A, uint32_t B); #endif // XOR_PROBLEMS_Hxor_problems.c
#include "xor_problems.h" uint32_t problem1_1(uint32_t A, uint32_t B) { uint32_t count = 0; for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++) { if((A ^ B) & 1) { count++; } A >>= 1; B >>= 1; } return count; } uint32_t problem1_2(uint32_t A, uint32_t B) { uint32_t xor_result = A ^ B; uint32_t count = 0; for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++) { if(xor_result & 1) { count++; } xor_result >>= 1; } return count; }test_xor_problems.c
#include "unity.h" #include "xor_problems.h" void setUp(void) { } void tearDown(void) { } void test_xor_problems1_example(void) { uint32_t x = 10; uint32_t y = 7; TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(3, problem1_1(x,y)); TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(3, problem1_2(x,y)); } void test_xor_problems1_example2(void) { uint32_t x = 0; uint32_t y = 0; TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(0, problem1_1(x,y)); TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(0, problem1_2(x,y)); } void test_xor_problems1_example3(void) { uint32_t x = 10; uint32_t y = 5; TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(4, problem1_1(x,y)); TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(4, problem1_2(x,y)); }Run test and result
ceedling test:xor_problems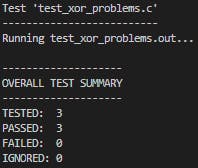
- Problem2: Every element appears twice except for one in given array. Find the single one. Assume array size is odd number. Reference: leetcode.com/problems/single-number
example#1 Input: [2, 5, 9, 9, 5] Output: 2
example#2 Input: [0] Output: 0
uint32_t problem2(uint32_t * arr, uint32_t arr_size)
{
uint32_t single_one = arr[0];
//Implement the logic
return single_one;
}
- Implementation and test
Hint: A XOR A = 0, A XOR 0 = A.
A XOR A XOR B = ?
0 XOR B = B
Single one is B
Add function prototype in xor_problems.h
uint32_t problem2(uint32_t * arr, uint32_t arr_size);Add function in xor_problems.c
uint32_t problem2(uint32_t * arr, uint32_t arr_size) { uint32_t single_one = arr[0]; for(uint32_t i = 1; i < arr_size; i++) { single_one ^= arr[i]; } return single_one; }Add test cases in test_xor_problems.c
void test_xor_problems2_example1(void) { uint32_t arr[] = {2, 5, 9, 9, 5}; TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(2, problem2(arr,5)); } void test_xor_problems2_example2(void) { uint32_t arr[] = {0}; TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(0, problem2(arr,1)); }Run test and result
ceedling test:xor_problems